Last Updated on June 25, 2025 by Jocelyn
Strawberries are tasty fruits loved worldwide for their bright red color, sweet flavor, and pleasant smell.
Rich in vitamins, they have been grown since the 1600s in France and are now an important part of farming and healthy diets.
The lifecycle of a strawberry plant begins with a tiny seed. When planted in garden soil or pots, the seed grows into a small green plant.
As it matures, it sends out special stems called runners that help the plant spread and create new ones.
Next, the plant produces flowers. Once pollinated, these flowers develop into green berries that slowly ripen, turning red and gaining their juicy sweetness and aroma.
The plant becomes dormant during colder months and starts the cycle again each year, making it a popular choice for home gardens.
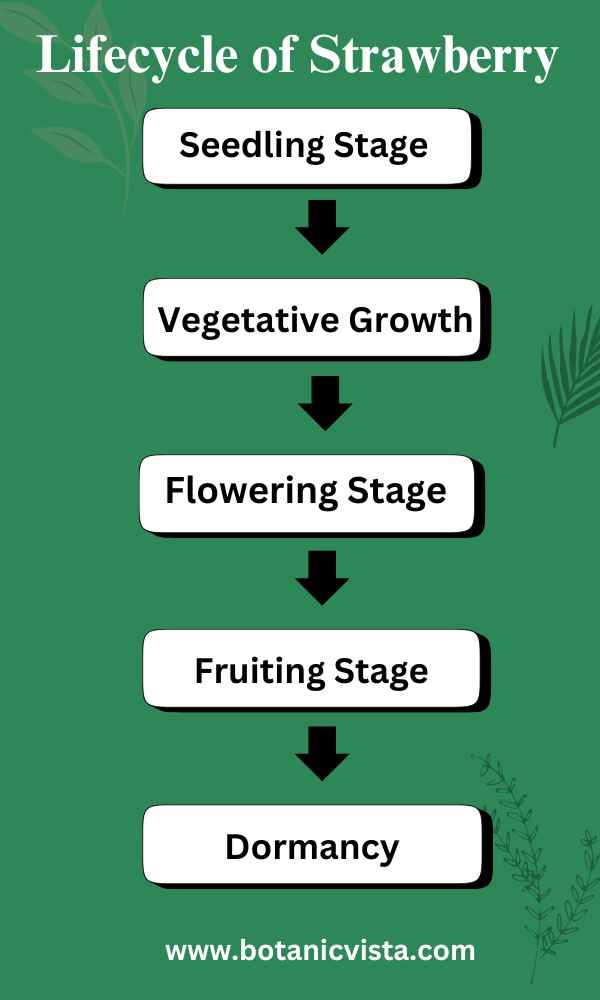
Table of Contents
Toggle5 Stages of Strawberry Growth
Strawberries grow through five distinct stages, each vital for producing healthy, delicious fruit. Starting from planting and moving through flowering and fruiting, every stage requires specific care.
Understanding these phases helps ensure a bountiful and high-quality harvest.
1. Seedling Stage
In the spring, tiny strawberry seeds begin to germinate. Albion and Seascape varieties are often chosen for their excellent fruit. Baby plants sprout from the seeds, producing small leaves and developing tiny root balls.
These seedlings need loamy soil and water to grow well. The seedling stage, which lasts about eight weeks, is crucial because this is when the roots start to establish themselves.
To avoid transplant shock, gently transplant these seedlings into prepared planting holes. The soil should be moist to support the growth of bare root crowns.
During this stage, the plants use their energy to build root systems and adjust to their new environment.
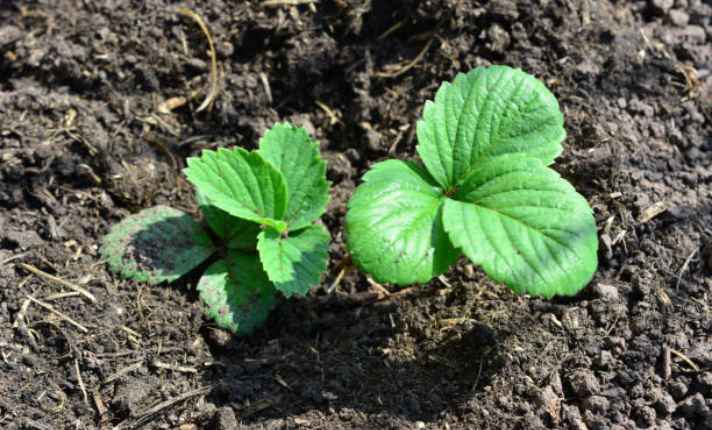

2. Vegetative Growth
The vegetative stage lasts about 8-12 weeks. During this period, the seedling grows roots and foliage. The roots absorb moisture and nutrients from the soil, while the leaves use photosynthesis to make food for the plant.
It’s crucial to provide plenty of nitrogen fertilizer and ensure the soil stays moist. As the plant matures, it develops shoots and runners, which help expand the strawberry patch.
This stage sets the foundation for a healthy plant capable of producing juicy berries in the later stages.
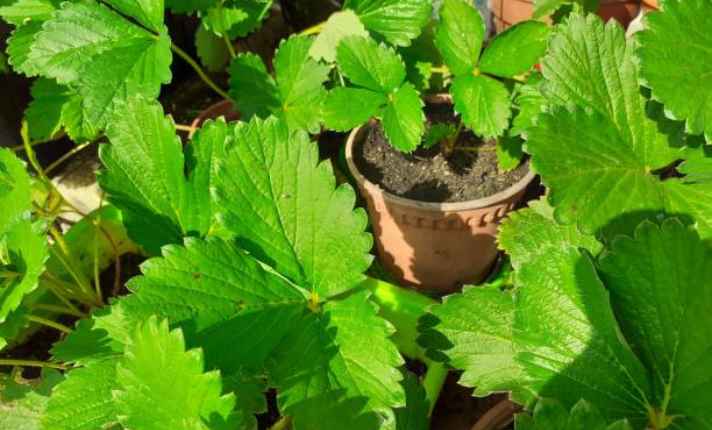

3. Flowering Stage
This phase begins as the weather starts to warm up, usually around mid-summer. The flowering stage typically lasts 12-14 days.
Strawberry plants are day-neutral. They will flower and produce fruit regardless of the daylight hours. However, the amount of light they receive each day still plays a beneficial role in their growth.
Flowers will appear on the plants, attracting pollinators like bees. These are beneficial as they help with pollination.
Gardeners often notice a shift in the plant’s energy towards producing beautiful blossoms. These flowers can be pink, white, or even bright yellow, depending on the variety.
Interplanting strawberries with Alyssum helps attract more pollinators. June-bearing varieties are popular because they produce a sufficient amount of fruit all at once, usually around June.

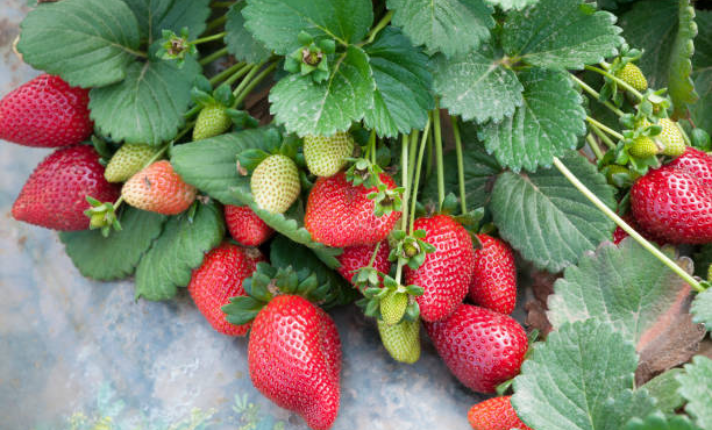
4. Fruiting Stage
The fruiting stage of strawberries starts 60 to 90 days after planting. You’ll see the first green berries, which change to red as they mature.
Different types of strawberries bear fruit at different times. June-bearing strawberries produce a large harvest in early summer, while day-neutral and everbearing varieties are produced continuously throughout the season.
To ensure quality, pick the ripest fruits to promote more flowering and fruiting. Flowers appear four to six weeks before fruits mature.
Harvesting every few days is essential to prevent overripe, mushy, or moldy berries, which can encourage disease and prevent continuous production.
June-bearing strawberries may not have significant volumes after their peak, but they are still important. Everbearing and day-neutral varieties ensure a steady harvest.
Proper timing and continuous picking are key to enjoying fresh strawberries throughout the season.

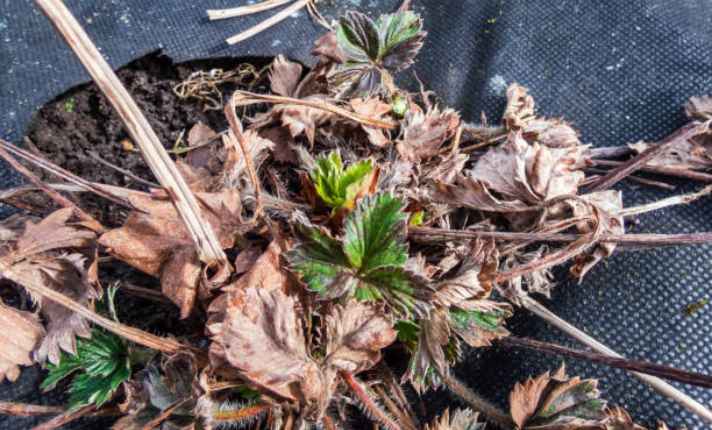
5. Dormancy
When strawberry plants enter dormancy in winter, they prepare for the next growing season. The foliage and leaves may wither and die, but the crowns and roots stay alive.
This stage helps the plants survive hard frost and cold temperatures, conserving energy and storing nutrients for spring.
Adding mulch and pruning protects the plants during this time. As spring approaches, the dormant plants wake up, new leaves and stems grow, and flowers start to develop.
Frost-tolerant strawberry plants handle hard frost well, repeating this cycle each year, ensuring they thrive through the changing seasons.

Tips for Speed up Strawberry Growth
To speed up the growth of strawberry plants, you need to create the right conditions and use some smart techniques. Make sure the soil is well-prepared, water correctly, and protect the young plants.
Here is a detailed guide:
| Aspect | Tips and Tricks |
| Starting | Use bare root crowns and keep them in the refrigerator to maintain dormancy. |
| Soaking | Soak the roots in a diluted kelp solution before planting. |
| Plugs and Bright Spots | Use plugs and place them on a bright windowsill, in a greenhouse, or under outdoor conditions. |
| Soil Preparation | Ensure the soil is rich with compost and use a broad fork to loosen and aerate the strawberry beds. Make mounds for good drainage and moisture control. |
| Protection | Protect the shallow-rooted plants from bad weather using row fabric and mulch. |
| Containers and Frost Date | Keep them in containers until the frost date has passed and the soil is warm. |
FAQ’s
Q: What Is the Cycle of a Strawberry?
A: The life cycle of a strawberry starts with planting seeds. In about 30 days, the seeds sprout into plants. Strawberry plants are perennials, so they come back every year.
After getting established, they produce flowers that turn into strawberries, which you can harvest each year.
Q: How Many Strawberries Do You Get From One Plant?
A: A healthy strawberry plant can produce between 150 to 400 strawberries in a single season. The exact number depends on factors like variety, care, and growing conditions.
Q: How Long Does It Take for a Strawberry Plant to Produce Fruit?
A: It takes about 60 to 90 days for a strawberry plant to grow from a seed to a mature plant and produce delicious berries.
The duration depends on conditions like light, temperature, watering, and fertilizing. Pay attention to these factors for a successful harvest.
Q: How Long Do Strawberry Plants Last in Pots?
A: Strawberry plants can live for about three years in pots. Use good potting soil, a container with a drainage hole, and ensure regular repotting for healthy growth. Snip runners if you don’t want new plants.
Q: What Month Is Best to Plant Strawberries?
A: Strawberries can be planted in March for a spring harvest. In an unheated polytunnel, plant in December to get fruit by spring. Use a heated greenhouse for early strawberries.
Conclusion
Strawberries grow in moist, rich soil with plenty of moisture. Plants can be started from bare-root crowns or plugs.
In the first few weeks, tiny flowers appear. After a few more weeks, berries begin to ripen. Within weeks, the fruits are ready to be harvested. Gardeners can enjoy many harvests during the season, especially with day-neutral varieties like ‘Albion’ and ‘Seascape’.
Strawberry plants need protection from harsh weather and thrive in the right conditions. They stay productive for many months. Growing strawberries is rewarding and fun for everyone.
Read More:

